Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00010
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Enalapril
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; Enalapril (INN); Enalapril (TN); N-[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]-L-alanyl-L-proline; N-{(1S)-1-[(ethyloxy)carbonyl]-3-phenylpropyl}-L-alanyl-L-proline; Renitec (TN); Vasotec; Vasotec (TN)
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | High blood pressure [ICD11: BA00] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
|||||
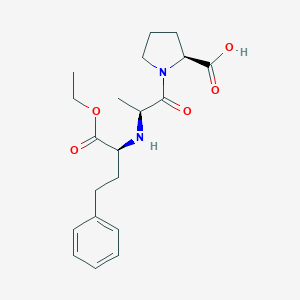
| Structure |
|
 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C20H28N2O5
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCOC(=O)C(CCC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(C)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)O
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H28N2O5/c1-3-27-20(26)16(12-11-15-8-5-4-6-9-15)21-14(2)18(23)22-13-7-10-17(22)19(24)25/h4-6,8-9,14,16-17,21H,3,7,10-13H2,1-2H3,(H,24,25)/t14-,16-,17-/m0/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
GBXSMTUPTTWBMN-XIRDDKMYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 75847-73-3
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 376.4 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.9 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | Rotatable Bond Count | 10 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |||
| XLogP |
-0.1
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103179319
, 103928457
, 11112847
, 11335583
, 11360822
, 11364201
, 11366763
, 11369325
, 11372634
, 11373494
, 11377487
, 113955320
, 11461794
, 11485085
, 11489271
, 11491293
, 11491823
, 11495121
, 127931871
, 134358398
, 135012773
, 137100856
, 140098266
, 14779899
, 14877707
, 17185069
, 29214998
, 39404326
, 46507920
, 47365119
, 47588933
, 47588934
, 47810682
, 48110391
, 48184936
, 48415941
, 49698433
, 50073899
, 50103938
, 50103939
, 53787340
, 57362754
, 75931775
, 7979157
, 89736144
, 9191
, 92309084
, 93166909
, 96024588
, 99313640
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:4784
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1A2 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| PEPT1 | Transporter Info | Peptide transporter 1 | Substrate | [5] | ||
| PEPT2 | Transporter Info | Peptide transporter 2 | Substrate | [6] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Enalapril was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Vectorial transport of enalapril by Oatp1a1/Mrp2 and OATP1B1 and OATP1B3/MRP2 in rat and human livers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jul;318(1):395-402. | |||||
| 3 | Uptake of enalapril and expression of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1 in zonal, isolated rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000 Jul;28(7):801-6. | |||||
| 4 | The modified dipeptide, enalapril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, is transported by the rat liver organic anion transport protein. Hepatology. 1998 Nov;28(5):1341-6. | |||||
| 5 | The intestinal H+/peptide symporter PEPT1: structure-affinity relationships. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2004 Jan;21(1):53-60. | |||||
| 6 | Ethanol inhibits functional activity of the human intestinal dipeptide transporter hPepT1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 May;32(5):777-84. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
