Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00367
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Azithromycin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Azasite (TN); Azibiot; Azifine; Azithramycine; Azithromycin (INN); Azithromycin (TN); Zitrocin
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Traveler's diarrhea [ICD11: ME05.1] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Middle ear infections [ICD11: AB0Z] | Approved | [1] | ||||
| Strep throat [ICD11: 1B51] | Approved | [1] | ||||
| Pneumonia [ICD11: CA40] | Approved | [1] | ||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
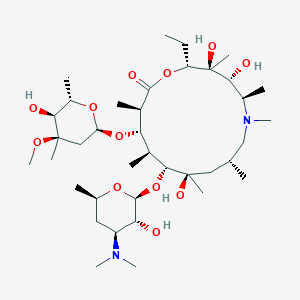 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C38H72N2O12
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CCC1C(C(C(N(CC(CC(C(C(C(C(C(=O)O1)C)OC2CC(C(C(O2)C)O)(C)OC)C)OC3C(C(CC(O3)C)N(C)C)O)(C)O)C)C)C)O)(C)O
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C38H72N2O12/c1-15-27-38(10,46)31(42)24(6)40(13)19-20(2)17-36(8,45)33(52-35-29(41)26(39(11)12)16-21(3)48-35)22(4)30(23(5)34(44)50-27)51-28-18-37(9,47-14)32(43)25(7)49-28/h20-33,35,41-43,45-46H,15-19H2,1-14H3/t20-,21-,22+,23-,24-,25+,26+,27-,28+,29-,30+,31-,32+,33-,35+,36-,37-,38-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
MQTOSJVFKKJCRP-BICOPXKESA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 83905-01-5
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 749 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 180 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 52 | Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 | |||
| XLogP |
4
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:2955
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | |
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Azithromycin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Possible involvement of the drug transporters P glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein Mrp2 in disposition of azithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Mar;48(3):809-14. | |||||
| 3 | Resveratrol modifies biliary secretion of cholephilic compounds in sham-operated and cholestatic rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov 21;23(43):7678-7692. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
