Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00455
|
|||||
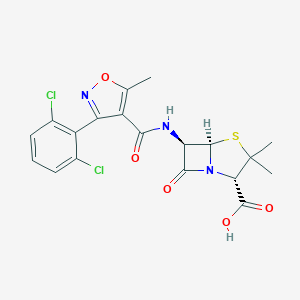
| Drug Name |
Dicloxacillin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(2S,5R,6R)-6-({[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-({[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 3-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolylpenicillin; 6-(3-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 6-(3-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)penicillanic acid; 6beta-{[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carboxamido}-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carboxylic acid; BRL 1702; Dichloroxacillin; Diclocil (TN); Diclossacillina; Diclossacillina [DCIT]; Dicloxaciclin; Dicloxacilin; Dicloxacilina; Dicloxacilina [INN-Spanish]; Dicloxacillin (USAN/INN); Dicloxacillin [USAN:INN:BAN]; Dicloxacillin sodium; Dicloxacillin, Monosodium Salt, Mono-Hydrate; Dicloxacilline; Dicloxacilline [INN-French]; Dicloxacillinum; Dicloxacillinum [INN-Latin]; Dicloxacycline; Dycill; Dynapen; Maclicine; Methyldichlorophenylisoxazolylpenicillin; Pathocil; R-13423
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Susceptible gram-positive bacteria infections [ICD11: 1A00-1H0Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C19H17Cl2N3O5S
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C(=NO1)C2=C(C=CC=C2Cl)Cl)C(=O)NC3C4N(C3=O)C(C(S4)(C)C)C(=O)O
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H17Cl2N3O5S/c1-7-10(12(23-29-7)11-8(20)5-4-6-9(11)21)15(25)22-13-16(26)24-14(18(27)28)19(2,3)30-17(13)24/h4-6,13-14,17H,1-3H3,(H,22,25)(H,27,28)/t13-,14+,17-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
YFAGHNZHGGCZAX-JKIFEVAISA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 3116-76-5
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 470.3 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 138 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 | |||
| XLogP |
2.9
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103234555
, 104133803
, 104344973
, 11335833
, 11361072
, 11363826
, 11366388
, 11368950
, 11371491
, 11374192
, 11377112
, 11462044
, 11466478
, 11467598
, 11484777
, 11486175
, 11488797
, 11490202
, 11492322
, 11494746
, 117541882
, 124766323
, 134222806
, 134337731
, 134981835
, 135912430
, 136357162
, 137003736
, 140093221
, 142567322
, 14960168
, 29286044
, 46508182
, 47216776
, 47440256
, 47736481
, 47810752
, 47810753
, 48259229
, 48334496
, 48415884
, 50064670
, 50783422
, 57304808
, 57330050
, 7849407
, 7979067
, 8163742
, 85788067
, 9165
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:4511
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [2] | |
| PEPT1 | Transporter Info | Peptide transporter 1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| PEPT2 | Transporter Info | Peptide transporter 2 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Dicloxacillin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Can the enhanced renal clearance of antibiotics in cystic fibrosis patients be explained by P-glycoprotein transport? Pharm Res. 2002 Apr;19(4):457-62. | |||||
| 3 | Transport characteristics of a novel peptide transporter 1 substrate, antihypotensive drug midodrine, and its amino acid derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Jul;318(1):455-60. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
