Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00523
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Crizotinib
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Xalkori (TN); novel ALK inhibitors
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD11: 2C25] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
|
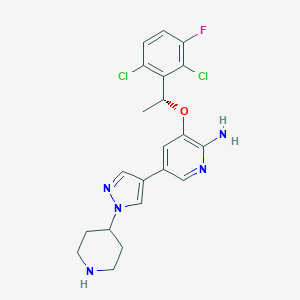 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C21H22Cl2FN5O
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C1=C(C=CC(=C1Cl)F)Cl)OC2=C(N=CC(=C2)C3=CN(N=C3)C4CCNCC4)N
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H22Cl2FN5O/c1-12(19-16(22)2-3-17(24)20(19)23)30-18-8-13(9-27-21(18)25)14-10-28-29(11-14)15-4-6-26-7-5-15/h2-3,8-12,15,26H,4-7H2,1H3,(H2,25,27)/t12-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
KTEIFNKAUNYNJU-GFCCVEGCSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 877399-52-5
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 450.3 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 78 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |||
| XLogP |
3.7
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103728028
, 104161043
, 119526687
, 121278669
, 124490471
, 124756975
, 125163780
, 125299329
, 126659900
, 131407280
, 135264650
, 135668295
, 135727397
, 136345871
, 136367829
, 136920405
, 137232008
, 137275901
, 141226597
, 143499147
, 152040652
, 152134626
, 152237527
, 152258843
, 152344161
, 160644611
, 160647693
, 160815247
, 160969694
, 162010188
, 162010189
, 162011538
, 162196520
, 162927269
, 163565316
, 163590241
, 164041842
, 164193931
, 165245564
, 16729581
, 170497919
, 174531154
, 175265614
, 23733583
, 74374126
, 75543391
, 93581001
, 99309272
, 99437209
, 99445171
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:64310
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Crizotinib was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 15;19(6):1458-66. | |||||
| 3 | Increased oral availability and brain accumulation of the ALK inhibitor crizotinib by coadministration of the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) inhibitor elacridar. Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 15;134(6):1484-94. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
