Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR01165
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Gatifloxacin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(+-)-1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; AM 1155; AM-1155; AM-1155 (*Sesquihydrate*); BMS 206584-01; BMS-206584; BMS-206584-01; Bonoq; CG 5501;PD 135432; CG-5501; GTFX; Gaity; Gatiflo; Gatiflo (TN); Gatiflo,Tequin and Zymar, Gatifloxacin; Gatifloxacin & Gamma Interferon; Gatifloxacin (INN); Gatifloxacin (TN); Gatifloxacin [USAN:INN]; Gatilox; Gatiquin; Gatispan; PD-135432; PD135432; Tequin; Tequin (TN); Tequin in dextrose 5% in plastic container; Zymar; Zymar (TN); Zymaxid; Zymer; Zymer (TN)
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Bacterial infections [ICD11: 1A00-1H0Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinfective Agents
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
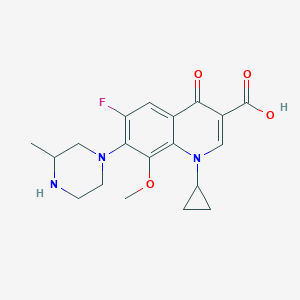 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C19H22FN3O4
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1CN(CCN1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4CC4)F
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H22FN3O4/c1-10-8-22(6-5-21-10)16-14(20)7-12-15(18(16)27-2)23(11-3-4-11)9-13(17(12)24)19(25)26/h7,9-11,21H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
XUBOMFCQGDBHNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 112811-59-3
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 375.4 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.1 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |||
| XLogP |
-0.7
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
103165247
, 103905240
, 104011321
, 104170200
, 11364853
, 11367415
, 11369977
, 11372016
, 11374751
, 11378145
, 11484089
, 11488303
, 11490814
, 11492941
, 11495723
, 12014137
, 14755600
, 25623206
, 26612698
, 26680481
, 26719627
, 26748958
, 26748959
, 29224431
, 3206265
, 4404784
, 46386695
, 46506159
, 47662548
, 47736764
, 49831421
, 50068220
, 50123177
, 57322743
, 618409
, 642042
, 77936610
, 7979373
, 8153306
, 85279062
, 85789262
, 861394
, 87322631
, 92124759
, 92307956
, 92309206
, 92711370
, 96024704
, 9863
, 99437219
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:5280
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1A2 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Gatifloxacin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Uptake and intracellular release kinetics of liposome formulations in glioma cells. Int J Pharm. 2010 Aug 16;395(1-2):251-9. | |||||
| 3 | Identification of influx transporter for the quinolone antibacterial agent levofloxacin. Mol Pharm. 2007 Jan-Feb;4(1):85-94. | |||||
| 4 | Interaction of gatifloxacin with efflux transporters: a possible mechanism for drug resistance. Int J Pharm. 2010 Aug 16;395(1-2):114-21. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
