Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR01468
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Amphotericin B
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
amphotericin b; Amphotericine B; Amphotericin; Amfotericina B; Amphotericinum B; Fungizone; Halizon; Amphocin; AMPH-B; Liposomal Amphotericin B; Fungilin; Amphozone; Ambisome; Abelcet; Ampho-Moronal; Amphotericin-B; Amphortericin B; UNII-7XU7A7DROE; Amphotec; Abelecet; Mysteclin-F; MFCD00877763; 7XU7A7DROE; NCGC00090808-01; DSSTox_CID_2601; NSC 527017; DSSTox_RID_76653; DSSTox_GSID_22601; Amphomoronal; Fungisome; Fungisone; Amphotericinum B [INN-Latin]; Amfotericina B [INN-Spanish]; Amphotericine B [INN-French]; CCRIS 5963
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Fungal infections [ICD11: 1F20-1F2Z] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antifungal Agents
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
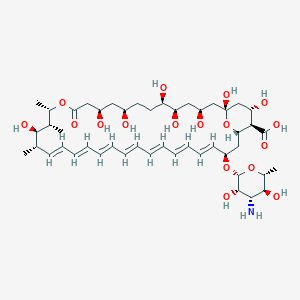 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C47H73NO17
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1C=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC(CC2C(C(CC(O2)(CC(CC(C(CCC(CC(CC(=O)OC(C(C1O)C)C)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)C(=O)O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)C)O)N)O
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C47H73NO17/c1-27-17-15-13-11-9-7-5-6-8-10-12-14-16-18-34(64-46-44(58)41(48)43(57)30(4)63-46)24-38-40(45(59)60)37(54)26-47(61,65-38)25-33(51)22-36(53)35(52)20-19-31(49)21-32(50)23-39(55)62-29(3)28(2)42(27)56/h5-18,27-38,40-44,46,49-54,56-58,61H,19-26,48H2,1-4H3,(H,59,60)/b6-5+,9-7+,10-8+,13-11+,14-12+,17-15+,18-16+/t27-,28-,29-,30+,31+,32+,33-,34-,35+,36+,37-,38-,40+,41-,42+,43+,44-,46-,47+/m0/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
APKFDSVGJQXUKY-INPOYWNPSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 1397-89-3
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 924.1 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 320 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 65 | Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 12 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 | |||
| XLogP |
0
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID | ||||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:2682
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [2] | |
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Amphotericin-B was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Carotenoids reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells by interfering with ABC-transporters. Phytomedicine. 2012 Aug 15;19(11):977-87. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
