Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00013
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Nilotinib
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Nilotinib; Tasigna; AMN107; AMN 107; AMN-107; Nilotinib(AMN-107); Nilotinib (AMN-107); UNII-F41401512X; 4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]benzamide; 4-Methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-N-(5-(4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide; CHEMBL255863; C28H22F3N7O; HHZIURLSWUIHRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N; NSC747599; MFCD09833716
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Chronic myelogenous leukemia [ICD11: 2A20.0] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
|||||
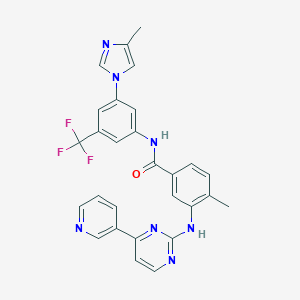
| Structure |
|
 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C28H22F3N7O
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC2=CC(=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)N3C=C(N=C3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H22F3N7O/c1-17-5-6-19(10-25(17)37-27-33-9-7-24(36-27)20-4-3-8-32-14-20)26(39)35-22-11-21(28(29,30)31)12-23(13-22)38-15-18(2)34-16-38/h3-16H,1-2H3,(H,35,39)(H,33,36,37)
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
HHZIURLSWUIHRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 641571-10-0
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 529.5 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 97.6 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 | Rotatable Bond Count | 6 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |||
| XLogP |
4.9
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID | ||||||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:52172
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | BCRP | Transporter Info | Breast cancer resistance protein | Substrate | [2] | |
| MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Nilotinib was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Interaction of nilotinib, dasatinib and bosutinib with ABCB1 and ABCG2: implications for altered anti-cancer effects and pharmacological properties. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;158(4):1153-64. | |||||
| 3 | Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 15;19(6):1458-66. | |||||
| 4 | KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D353-D361. (dg:DG01665) | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
