Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00124
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Fluvastatin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(+)-(3R,5S)-fluvastatin; (-)-(3S,5R)-fluvastatin; (3R,5R,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5R,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-rel-7-[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid; (3S,5R,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3S,5R,6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (6E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (E)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (E,3R,5S)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (E,3S,5R)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (Z,3R,5S)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; 7-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-indol-2-yl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoate; 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-propan-2-ylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; Canef; Canef(TN); Cranoc; Fluindostatin; Fluvas; Fluvas (TN); Fluvastatin & Primycin; Fluvastatin (INN); Fluvastatin [INN:BAN]; Fluvastatina; Fluvastatina [INN-Spanish]; Fluvastatine; Fluvastatine [INN-French]; Fluvastatinum; Fluvastatinum [INN-Latin]; Lescol; Lescol (TN); Lescol XL; Vastin (TN); XU 62320; XU-62320
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Hypercholesterolemia [ICD11: 5C80.0] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticholesteremic Agents
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
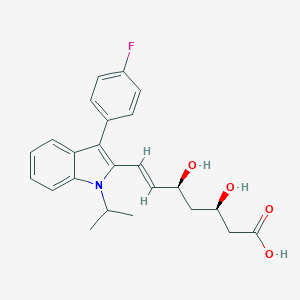 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C24H26FNO4
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)N1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=C1C=CC(CC(CC(=O)O)O)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)F
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H26FNO4/c1-15(2)26-21-6-4-3-5-20(21)24(16-7-9-17(25)10-8-16)22(26)12-11-18(27)13-19(28)14-23(29)30/h3-12,15,18-19,27-28H,13-14H2,1-2H3,(H,29,30)/b12-11+/t18-,19-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
FJLGEFLZQAZZCD-MCBHFWOFSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 93957-54-1
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 411.5 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 82.7 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | Rotatable Bond Count | 8 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |||
| XLogP |
3.5
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
100024002
, 10299838
, 103043439
, 103293858
, 104170157
, 104635874
, 10584685
, 10852031
, 117368355
, 121362529
, 126667384
, 130408282
, 131378297
, 135650279
, 136352753
, 136910868
, 137201916
, 143038598
, 144075757
, 144213082
, 14981407
, 152164360
, 152245639
, 162221786
, 163620805
, 163686130
, 165235894
, 172080782
, 175269733
, 175611054
, 176253518
, 176484235
, 24775765
, 36888653
, 46505668
, 47291222
, 48413791
, 48416032
, 49835750
, 49857384
, 50758963
, 53787111
, 56312811
, 56313633
, 57404724
, 7979295
, 822161
, 85856290
, 91613309
, 92308982
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:5136
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | BCRP | Transporter Info | Breast cancer resistance protein | Substrate | [2] | |
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| OATP2B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 2B1 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [5] | ||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | ||||||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 1.4 microM | Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells-OATP1B1 | [4] | |
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 3.5 microM | Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells-OATP1B1 | [4] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 31.1 microM | Oocytes-OATP1B1 | [6] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Km = 7 microM | Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCKII)-OATP1B3 | [7] | ||
| OATP2B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 0.75 microM | Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293)-OATP2B1 | [4] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Fluvastatin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Evaluation of the usefulness of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) knockout mice and BCRP inhibitor-treated monkeys to estimate the clinical impact of BCRP modulation on the pharmacokinetics of BCRP substrates. Pharm Res. 2015 May;32(5):1634-47. | |||||
| 3 | SLCO1B1 polymorphism and sex affect the pharmacokinetics of pravastatin but not fluvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Oct;80(4):356-66. | |||||
| 4 | Substrate-dependent drug-drug interactions between gemfibrozil, fluvastatin and other organic anion-transporting peptide (OATP) substrates on OATP1B1, OATP2B1, and OATP1B3. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007 Aug;35(8):1308-14. | |||||
| 5 | A novel screening strategy to identify ABCB1 substrates and inhibitors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;379(1):11-26. | |||||
| 6 | The effect of SLCO1B1*15 on the disposition of pravastatin and pitavastatin is substrate dependent: the contribution of transporting activity changes by SLCO1B1*15. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 May;18(5):424-33. | |||||
| 7 | Human hepatobiliary transport of organic anions analyzed by quadruple-transfected cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Oct;68(4):1031-8. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
