Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR00223
|
|||||
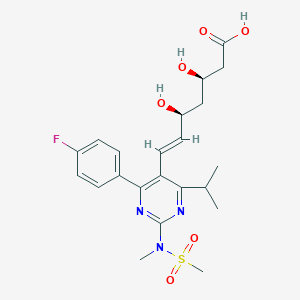
| Drug Name |
Rosuvastatin
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
(3R,5S,6E)-7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(ethyl(methylsulfonyl)amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-7-{4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-6-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl}-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (3R,5S,6E)-7-{4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]pyrimidin-5-yl}-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (E,3R,5R)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-6-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-5-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (E,3R,5S)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-6-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-5-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; (S-((R*,S*-(E)))-7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(methyl(methylsulfonyl) amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid, calcium salt (2:1); (S-(R*,S*-(E)))-7-(4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid, calcium salt (2:1); 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(ethyl(methylsulfonyl)amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-, (3R,5S,6E); 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-(methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino)-5-pyrimidinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-, calcium salt (2:1), (3R,5S,6E); AZD-4522; Astende; Bis[(E)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino] pyrimidin-5-yl](3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxyhelpt-6-enoic acid] calcium salt; Calcium (E,3R,5S)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-6-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-5-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate; Cirantan; Cresadex; Creston; Creston (TN);Crestor (TN); Crestor; Provisacor; Pyrimidine Compound, 26; Razel; Rosedex; Rosimol; Rosumed; Rosustatin; Rosuvas; Rosuvast; Rosuvastatin (INN); Rosuvastatin [INN]; Rosuvastatin calcium; Rosuvastatin calcium (JAN/USAN); Rosuvastatin calcium [USAN]; Rosuvastatin hemicalcium; Rosvel; Rovartal; S 4522; S-4522; Simestat; Sinlip; Vivacor; ZD 4522; ZD 4522, calcium salt; ZD-4522; ZD4522
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Hypercholesterolemia [ICD11: 5C80.0] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticholesteremic Agents
|
|||||
| Structure |
|
 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C22H28FN3O6S
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C1=NC(=NC(=C1C=CC(CC(CC(=O)O)O)O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)F)N(C)S(=O)(=O)C
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H28FN3O6S/c1-13(2)20-18(10-9-16(27)11-17(28)12-19(29)30)21(14-5-7-15(23)8-6-14)25-22(24-20)26(3)33(4,31)32/h5-10,13,16-17,27-28H,11-12H2,1-4H3,(H,29,30)/b10-9+/t16-,17-/m1/s1
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
BPRHUIZQVSMCRT-VEUZHWNKSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 287714-41-4
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 481.5 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 149 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 | Rotatable Bond Count | 10 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 | |||
| XLogP |
1.6
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
10299840
, 103556348
, 104635880
, 104829200
, 124637938
, 126680774
, 126731182
, 127315738
, 127315739
, 127315740
, 127315741
, 127315742
, 127315743
, 127315744
, 127315745
, 127315746
, 127315747
, 127315748
, 127315749
, 127315750
, 127315751
, 127315752
, 127315753
, 127315754
, 127315755
, 127315756
, 127315757
, 127315758
, 135084331
, 135650928
, 135723476
, 14810118
, 14834808
, 24775831
, 26612833
, 26680899
, 36888655
, 46509022
, 46518448
, 47960010
, 48035409
, 50070881
, 50122666
, 53790555
, 57404725
, 80442666
, 822168
, 88531873
, 92124833
, 96025178
|
|||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:38545
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | BCRP | Transporter Info | Breast cancer resistance protein | Substrate | [2] | |
| MRP2 | Transporter Info | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| NTCP | Transporter Info | Sodium/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide | Substrate | [3] | ||
| OAT3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporter 3 | Substrate | [4] | ||
| OATP1A2 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2 | Substrate | [3] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| OATP2B1 | Transporter Info | Organic anion transporting polypeptide 2B1 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | ||||||
| Drug-Transporter Activity Data | BCRP | Transporter Info | Km = 2.02 microM | Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293)-BCRP | [2] | |
| BCRP | Transporter Info | Km = 10.1 microM | Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCKII)-BCRP | [5] | ||
| NTCP | Transporter Info | Km = 65 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-NTCP | [3] | ||
| OAT3 | Transporter Info | Km = 7.4 microM | Oocytes-OAT3 | [4] | ||
| OATP1A2 | Transporter Info | Km = 2.6 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-OATP1A2 | [3] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 4 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-OATP1B1 | [3] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 7.3 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-OATP1B1 | [3] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 0.8 microM | Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293)-OATP1B1 | [2] | ||
| OATP1B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 8.5 microM | Oocytes-OATP1B1 | [6] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Km = 9.8 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-OATP1B3 | [3] | ||
| OATP1B3 | Transporter Info | Km = 14.2 microM | Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293)-OATP1B3 | [2] | ||
| OATP2B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 2.4 microM | Human cervical cancer cell line (Hela)-OATP2B1 | [3] | ||
| OATP2B1 | Transporter Info | Km = 6.42 microM | Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293)-OATP2B1 | [2] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Rosuvastatin was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | Involvement of multiple transporters in the hepatobiliary transport of rosuvastatin. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Oct;36(10):2014-23. | |||||
| 3 | Drug and bile acid transporters in rosuvastatin hepatic uptake: function, expression, and pharmacogenetics. Gastroenterology. 2006 May;130(6):1793-806. | |||||
| 4 | The contribution of organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 to the renal uptake of rosuvastatin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Sep;322(3):1221-7. | |||||
| 5 | Effect of silymarin supplement on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. Pharm Res. 2008 Aug;25(8):1807-14. | |||||
| 6 | Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in heart transplant recipients administered an antirejection regimen including cyclosporine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Aug;76(2):167-77. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
