Drug Information
| General Information | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
DR01336
|
|||||
| Drug Name |
Binimetinib
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
181R97MR71; 5-[(4-Bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide; 6-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methyl-3H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamide; 606143-89-9; ARRY 162; ARRY 438162; ARRY-162; ARRY-438162; Binimetinib (JAN/USAN); Binimetinib (MEK162, ARRY-162, ARRY-438162); Binimetinib [USAN:INN]; D0C4LF; MEK 162; MEK-162; MEK162; MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162); MEK162(Binimetinib); NVP-ME; UNII-181R97MR71
|
|||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||
| Indication | Melanoma [ICD11: 2C30] | Approved | [1] | |||
| Structure |
|
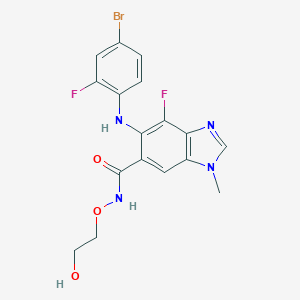 |
||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||
| Formula |
C17H15BrF2N4O3
|
|||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1C=NC2=C1C=C(C(=C2F)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)Br)F)C(=O)NOCCO
|
|||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H15BrF2N4O3/c1-24-8-21-16-13(24)7-10(17(26)23-27-5-4-25)15(14(16)20)22-12-3-2-9(18)6-11(12)19/h2-3,6-8,22,25H,4-5H2,1H3,(H,23,26)
|
|||||
| InChIKey |
ACWZRVQXLIRSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 606143-89-9
|
|||||
| Pharmaceutical Properties | Molecular Weight | 441.2 | Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.4 | ||
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | Rotatable Bond Count | 6 | |||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 | |||
| XLogP |
3.1
|
|||||
| PubChem CID | ||||||
| PubChem SID |
15294150
, 22663761
, 35560186
, 76385017
, 136920431
, 139722085
, 152256088
, 152258645
, 160647480
, 162011797
, 162108908
, 163750757
, 164042001
, 172919200
, 174006430
, 174529974
, 185990487
, 198988096
, 223386768
, 223705205
, 225848212
, 226876700
, 242590736
, 243963093
, 249565604
, 252215762
, 252450328
, 252554049
|
|||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||||
| DT(s) Transporting This Drug | BCRP | Transporter Info | Breast cancer resistance protein | Substrate | [2] | |
| P-GP | Transporter Info | P-glycoprotein 1 | Substrate | [2] | ||
| References | ||||||
| 1 | Binimetinib was approved by FDA. The official website of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019) | |||||
| 2 | The impact of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein on the brain pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a panel of MEK inhibitors. Int J Cancer. 2018 Jan 15;142(2):381-391. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Yin and Dr. Li.
